Spectral Enhancement is crucial process when analysing thin beds. The most common method to QC Spectral Enhancement is to use the slider in the Spectral Expression Tool. However, sometimes data quality can limit the true extent of enhancement that can be visualised, often characterised by washed out reflectors.
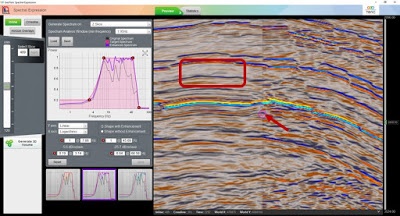
In order to get around this potential problem, we can use the Bedform Indicator attribute to help us. This attribute skeletonises the reflectors in the seismic data. It can be found in Workflows>Processes>Attributes>Trace Attributes>Bedform Indicator.
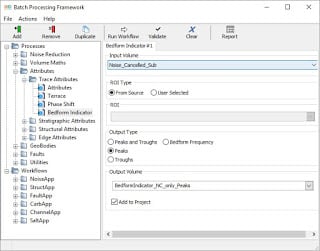
The image below shows the Bedform Indicator with the Peaks and Troughs option selected, which aids in visualising reflectors which appear more washed out.
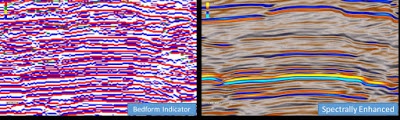
This can sometimes lead to an over-cluttered image, so in the example below only Peaks will be outputted. The Bedform Indicator should be run on both the noise cancelled volume and the spectrally enhanced volume, and a slice can be created to compare the two results.
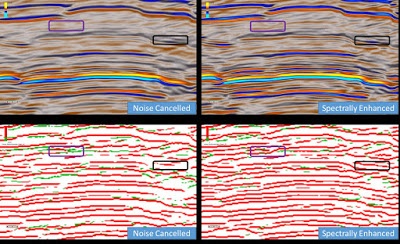
The red corresponds to positive reflectors while the green corresponds to positive doublets (often indicative of thin beds). As can be seen, some positive doublets now have been resolved fully into positive reflectors, helping to show the true extent of the spectral enhancement and allows the interpreter to explore the relationships between reflectors in more detail.
